Pneumonia is a bacterial disease caused by the type of bacteria called _________ / निमोनिया एक जीवाणु रोग है जो _________ नामक बैक्टीरिया के प्रकार के कारण होता है
(1) Bacilli / बेसिली
(2) Cocci / कोक्सी
(3) Sprilli / स्प्रिलि
(4) Vibrio / विब्रियो
(SSC CGL Tier-I (CBE) Exam.10.09.2016)
Answer / उत्तर :-
(2) Cocci / कोक्सी
Explanation / व्याख्या :-
निमोनिया एक जीवाणु रोग है जो स्ट्रेप्टोकोकस न्यूमोनिया, एक ग्राम-पॉजिटिव जीवाणु के कारण होता है। यह स्वस्थ लोगों के नाक और गले में रहता है और साँस द्वारा फेफड़ों में प्रवेश कर सकता है। निमोनिया के अन्य महत्वपूर्ण ग्राम-पॉजिटिव कारण स्टैफिलोकोकस ऑरियस और बैसिलस एंथ्रेसीस हैं।
जिस हवा में हम सांस लेते हैं उसमें कई तरह के बैक्टीरिया, वायरस और फंगस के कारण निमोनिया हो सकता है। अपने निमोनिया के कारण की पहचान करना उचित उपचार प्राप्त करने की दिशा में एक महत्वपूर्ण कदम हो सकता है।
जीवाणु
सबसे आम प्रकार के जीवाणु निमोनिया को न्यूमोकोकल निमोनिया कहा जाता है। न्यूमोकोकल निमोनिया स्ट्रेप्टोकोकस न्यूमोनिया रोगाणु के कारण होता है जो सामान्य रूप से ऊपरी श्वसन पथ में रहता है। यह हर साल 900,000 से अधिक अमेरिकियों को संक्रमित करता है।
बैक्टीरियल निमोनिया अपने आप हो सकता है या वायरल सर्दी या फ्लू होने के बाद विकसित हो सकता है। बैक्टीरियल निमोनिया अक्सर फेफड़े के सिर्फ एक हिस्से या लोब को प्रभावित करता है। जब ऐसा होता है, तो स्थिति को लोबार निमोनिया कहा जाता है। बैक्टीरियल निमोनिया के लिए सबसे बड़े जोखिम में सर्जरी से ठीक होने वाले लोग, श्वसन रोग या वायरल संक्रमण वाले लोग और कमजोर प्रतिरक्षा प्रणाली वाले लोग शामिल हैं।
कुछ प्रकार के बैक्टीरिया के कारण “एटिपिकल” निमोनिया होता है, जिसमें शामिल हैं:
- माइकोप्लाज्मा न्यूमोनिया, एक छोटा चौड़ा-फैला हुआ जीवाणु जो आमतौर पर 40 वर्ष से कम उम्र के लोगों को संक्रमित करता है, विशेष रूप से वे लोग जो भीड़-भाड़ वाली परिस्थितियों में रहते हैं और काम करते हैं। यह बीमारी अक्सर इतनी हल्की होती है कि इसका पता नहीं चल पाता और इसे कभी-कभी वॉकिंग निमोनिया भी कहा जाता है।
- क्लैमाइडोफिला न्यूमोनिया, जो आमतौर पर साल भर ऊपरी श्वसन संक्रमण का कारण बनता है, लेकिन इसके परिणामस्वरूप निमोनिया का हल्का रूप भी हो सकता है।
- लीजियोनेला न्यूमोफिला, जो लीजियोनेयर रोग नामक निमोनिया के एक खतरनाक रूप का कारण बनता है। अन्य जीवाणु निमोनिया के विपरीत, लेजिओनेला एक व्यक्ति से दूसरे व्यक्ति में नहीं फैलता है। रोग के प्रकोप को कूलिंग टावरों, व्हर्लपूल स्पा और बाहरी फव्वारों से दूषित पानी के संपर्क में आने से जोड़ा गया है।
- इन जीवाणुओं को “एटिपिकल” कहा जाता है क्योंकि इन जीवों के कारण होने वाले निमोनिया के लक्षण थोड़े अलग हो सकते हैं, छाती के एक्स-रे पर अलग दिखाई दे सकते हैं, या निमोनिया का कारण बनने वाले विशिष्ट बैक्टीरिया की तुलना में विभिन्न एंटीबायोटिक दवाओं का जवाब दे सकते हैं। भले ही इन संक्रमणों को “असामान्य” कहा जाता है, वे असामान्य नहीं हैं
बैक्टीरियल निमोनिया के लक्षणों की गंभीरता अलग-अलग हो सकती है। कुछ लोग केवल हल्के लक्षणों का अनुभव करते हैं, जबकि अन्य जीवन के लिए खतरा पैदा करने वाली जटिलताएं विकसित करते हैं।
अमेरिकन लंग एसोसिएशन के अनुसार, बैक्टीरियल निमोनिया के विशिष्ट लक्षणों में शामिल हैं:
- छाती में दर्द
- सांस लेने में कठिनाई
- एक खांसी जो पीले या हरे रंग का बलगम पैदा कर सकती है
- बुखार
- थकान
- ठंड लगना
जीवाणु निमोनिया के लक्षण दोनों में समान होते हैं
बच्चे और वयस्क। अमेरिकन एकेडमी ऑफ पीडियाट्रिक्स के अनुसार, बच्चे और शिशु सामान्य से अधिक रो सकते हैं, ऊर्जा कम कर सकते हैं और पीला दिखाई दे सकते हैं।
एक व्यक्ति जो निमोनिया के लक्षणों पर संदेह करता है, उसे चिकित्सा सहायता लेनी चाहिए। एक चिकित्सक को देखे बिना निमोनिया की एक विशेष प्रस्तुति का कारण निर्धारित करना मुश्किल हो सकता है।
चूंकि बैक्टीरियल और वायरल निमोनिया के उपचार अलग-अलग हैं, इसलिए उचित उपचार आहार चुनने के लिए सही कारण खोजना महत्वपूर्ण है।
जटिलताओं
बैक्टीरियल निमोनिया बच्चों और वयस्कों दोनों में जटिल हो सकता है। बैक्टीरियल निमोनिया से कोई भी जटिलताएं विकसित कर सकता है, लेकिन कमजोर प्रतिरक्षा प्रणाली वाले लोगों, छोटे बच्चों और बड़े वयस्कों में इसका जोखिम अधिक होता है।
जटिलताओं में निम्नलिखित शामिल हो सकते हैं:
- श्वसन विफलता: यह विकसित हो सकता है यदि फेफड़ों में ऑक्सीजन का स्तर बहुत कम हो जाता है या यदि कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड का स्तर बढ़ जाता है। यह अपर्याप्त सांस लेने की क्षमता के कारण हो सकता है, और श्वसन विफलता भी फेफड़ों के कार्य को पूरी तरह से बंद कर सकती है।
- सेप्सिस: यह तब होता है जब एक संक्रमण पूरे शरीर में अत्यधिक भड़काऊ प्रतिक्रिया का कारण बनता है।
- सेप्सिस कई अंगों में विफलता का कारण बन सकता है और जीवन के लिए खतरा हो सकता है।
- फेफड़े का फोड़ा: यह तब होता है जब फेफड़े में मवाद की एक संक्रमित जेब बन जाती है।
- एम्पाइमा: यह फुफ्फुस गुहा में मवाद का एक संक्रामक संग्रह है जो फेफड़ों के बाहर से घिरा होता है
कारण
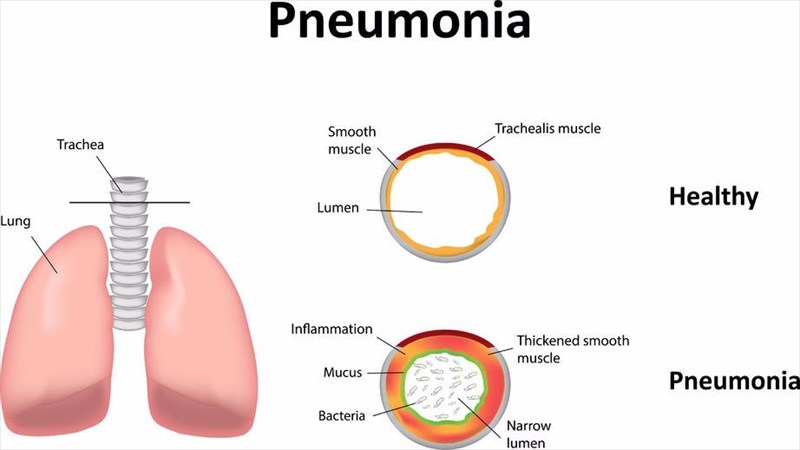
एल्वियोली नामक छोटी वायु थैली प्रत्येक फेफड़े के लोब के भीतर होती है। आम तौर पर, ये वायु थैली शरीर के गैस विनिमय में सहायता करती हैं, जबकि ऑक्सीजन को अंदर लेती हैं और कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड को बाहर निकालती हैं।
जब कोई व्यक्ति निमोनिया विकसित करता है, तो वायुकोशों में सूजन का अनुभव होता है, जिससे उनमें तरल पदार्थ भर सकता है। अगर हवा की थैली हवा के बजाय तरल पदार्थ से भर जाती है, तो सांस लेना मुश्किल हो सकता है।
कुछ मामलों में, फेफड़ों और शरीर के बाकी हिस्सों को पर्याप्त ऑक्सीजन नहीं मिल पाती है।
प्रकार
निमोनिया को अक्सर समुदाय-अधिग्रहित निमोनिया या अस्पताल-अधिग्रहित निमोनिया के रूप में वर्गीकृत किया जाता है। वर्गीकरण उस स्थान को संदर्भित करता है जिसमें किसी व्यक्ति ने संक्रमण प्राप्त किया था।
समुदाय-अधिग्रहित निमोनिया कहीं अधिक सामान्य प्रकार है। अन्य, कम सामान्य प्रकार हो सकते हैं, जैसे स्वास्थ्य देखभाल से जुड़े निमोनिया (एचसीएपी) और वेंटिलेटर से जुड़े निमोनिया (वीएपी)।
Pneumonia is a bacterial disease caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, a Gram-positive bacterium. It lives in the noses and throats of healthy people and can enter lungs through inhalation. Other important Gram-positive causes of pneumonia are Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus anthracis.
Pneumonia can be caused by a wide variety of bacteria, viruses and fungi in the air we breathe. Identifying the cause of your pneumonia can be an important step in getting the proper treatment.
Bacteria
The most common type of bacterial pneumonia is called pneumococcal pneumonia. Pneumococcal pneumonia is caused by the Streptococcus pneumoniae germ that normally lives in the upper respiratory tract. It infects over 900,000 Americans every year.
Bacterial pneumonia can occur on its own or develop after you’ve had a viral cold or the flu. Bacterial pneumonia often affects just one part, or lobe, of a lung. When this happens, the condition is called lobar pneumonia. Those at greatest risk for bacterial pneumonia include people recovering from surgery, people with respiratory disease or viral infection and people who have weakened immune systems.
Some types of bacteria cause what is known as “atypical” pneumonia, including:
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae, a tiny wide-spread bacterium that usually infects people younger than 40 years old, especially those living and working in crowded conditions. The illness is often mild enough to go undetected and is sometimes referred to as walking pneumonia.
- Chlamydophila pneumoniae, which commonly causes upper respiratory infections year-round, but can also result in a mild form of pneumonia.
- Legionella pneumophila, which causes a dangerous form of pneumonia called Legionnaire’s disease. Unlike other bacterial pneumonias, Legionella is not passed from person to person. Outbreaks of the disease have been linked to exposure to contaminated water from cooling towers, whirlpool spas, and outdoor fountains.
These bacteria are referred to as “atypical” because pneumonia caused by these organisms might have slightly different symptoms, appear different on a chest X-ray, or respond to different antibiotics than the typical bacteria that cause pneumonia. Even though these infections are called “atypical,” they are not uncommon.Symptoms
The severity of bacterial pneumonia symptoms can vary. Some people only experience mild symptoms while others develop life-threatening complications.
According to the American Lung Association, typical symptoms of bacterial pneumonia include:
- chest pain
- shortness of breath
- a cough that may produce yellow or green mucus
- fever
- tiredness
- chills
Symptoms of bacterial pneumonia tend to be similar in both
children and adults. According to the American Academy of Pediatrics, toddlers and infants may cry more than usual, have reduced energy, and appear pale.
A person who suspects symptoms of pneumonia should seek medical attention. The cause of a particular presentation of pneumonia can be difficult to determine without seeing a physician.
Since the treatments for bacterial and viral pneumonia are different, finding the correct cause is vital for choosing the appropriate treatment regimen.
Complications
Bacterial pneumonia might be complicated in both children and adults. Anyone can develop complications from bacterial pneumonia, but people with weaker immune systems, younger children, and older adults have a higher risk.
Complications may include the following:
- Respiratory failure: This might develop if oxygen levels in the lungs drop too low or if carbon dioxide levels spike. It can occur due to inadequate breathing ability, and respiratory failure may even cause lung function to stop completely.
- Sepsis: This occurs when an infection causes an overwhelming inflammatory response throughout the body. Sepsis can lead to failure in multiple organs and may be life-threatening.
- Lung abscess: This occurs when an infected pocket of pus forms in the lung.
- Empyema: This is an infectious collection of pus in the pleural cavity that surrounds the outside of lungs
Causes
Small air sacs called alveoli are within the lobes of each lung. Normally, these air sacs aid in the body’s gas exchange, while inhaling oxygen and exhaling carbon dioxide.
When a person develops pneumonia, the air sacs experience inflammation, which can cause them to fill with fluid. If the air sacs fill with fluid rather than air, breathing might become difficult.
In some cases, the lungs and the rest of the body may not get enough oxygen.
Types
Pneumonia is often classified as either community-acquired pneumonia or hospital-acquired pneumonia. The classification refers to the location in which a person acquired the infection.
Community-acquired pneumonia is the by far more the common type. Other, less common types can occur, such as healthcare-associated pneumonia (HCAP) and ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP).














No comments:
Post a Comment